Sierra Wireless GPS Setup
Sierra Wireless mPCIE modems often combine 3G/4G wireless connectivity along with GPS functionality
In this example we'll be using a MC7304 modem, for other models please check with the vendor to confirm GPS funtionality and GPS antenna type needed.
We'll start by installing the udev rule (20-modem-7304.rules) in /etc/udev/rules.d from the modem rule pack
This sets up shortcut references to allow us to consistently identify which of the ttyUSBx ports do which functions
root@raspberrypi:~# ls /dev/modem* -l lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jan 4 16:45 /dev/modemAT -> ttyUSB3 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jan 4 16:45 /dev/modemGPS -> ttyUSB2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jan 4 16:45 /dev/modemS0 -> ttyUSB1 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jan 4 16:45 /dev/modemS2 -> ttyUSB2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jan 4 16:45 /dev/modemS3 -> ttyUSB3
As the MC7304 modem has active GPS antenna compatibility we can use most of the gps aerials on the market or combo antennas.
After connecting up a combo antenna let's do a quick check to make sure the modem is configured correctly:
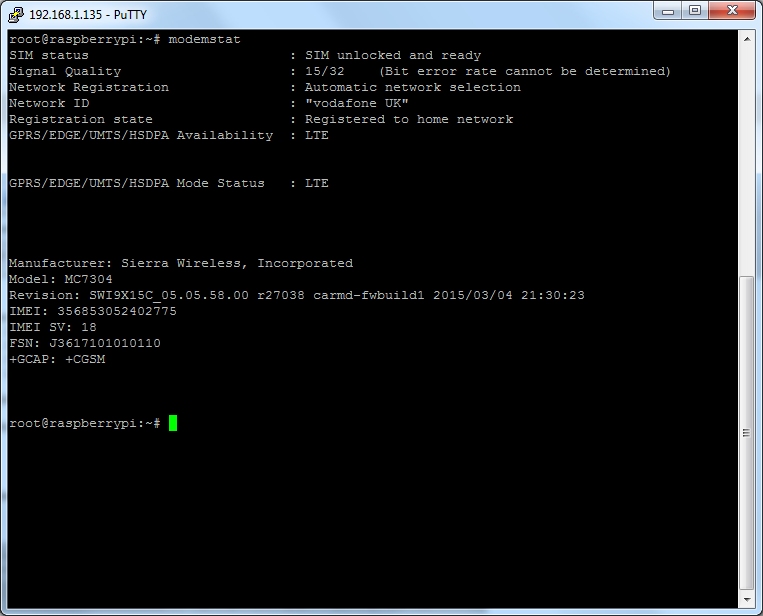
Having the SIM inserted and registered on the network gives the modem the correct time and can help with GPS fix time
There are a few commands we need to understand to correctly configure the GPS setup on the modem
AT+WANTGNSSPWR=1 Enable Active GPS antenna support (MC73xx) AT+WANT=1 Enable Active GPS antenna support (MC74xx) AT!GPSTRACK=1,255,1000,1000,1 Starts GPS service + NMEA Feed on /dev/modemGPS AT!GPSSTATUS? Get GPS fix status AT!GPSLOC? Run on AT command port to give a one-shot reading AT!GPSEND=0 Stops GPS Service + NMEA Feed on /dev/modemGPS
Let's drop into a minicom session and start up the GPS system. an un-assisted "First Fix" can take anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes, depending on the number of satellites visible.
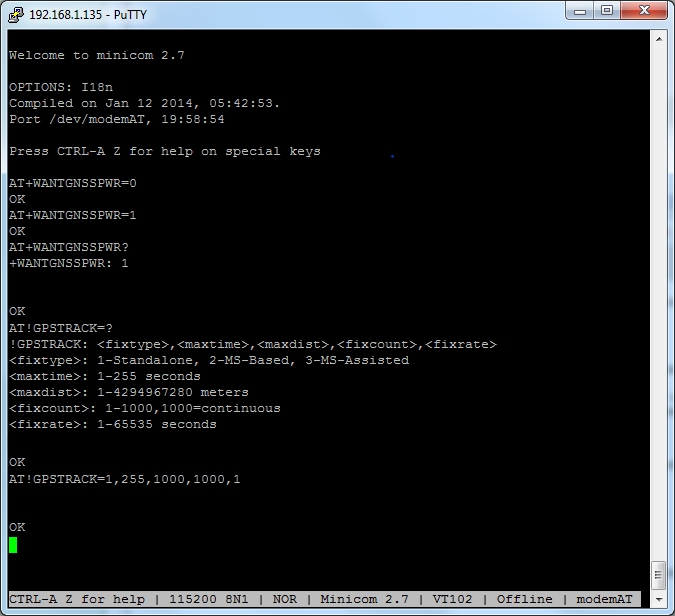
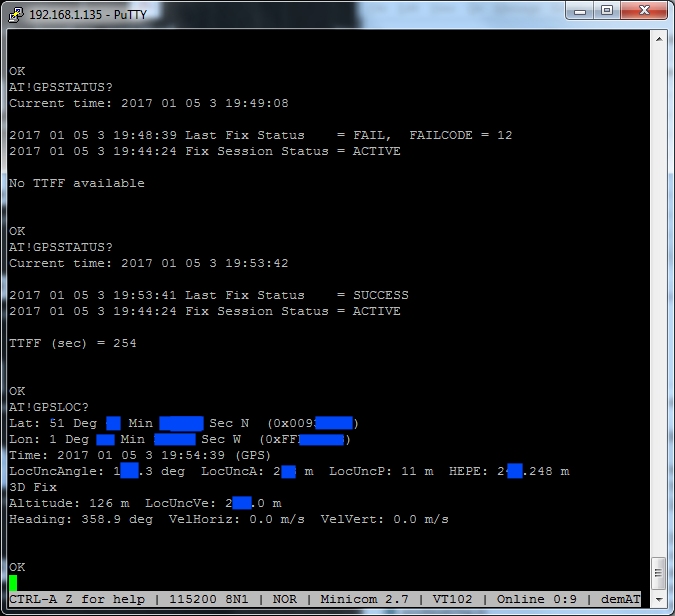
To enable the GPS NMEA feed on /dev/modemGPS you need as a one off to run the below :
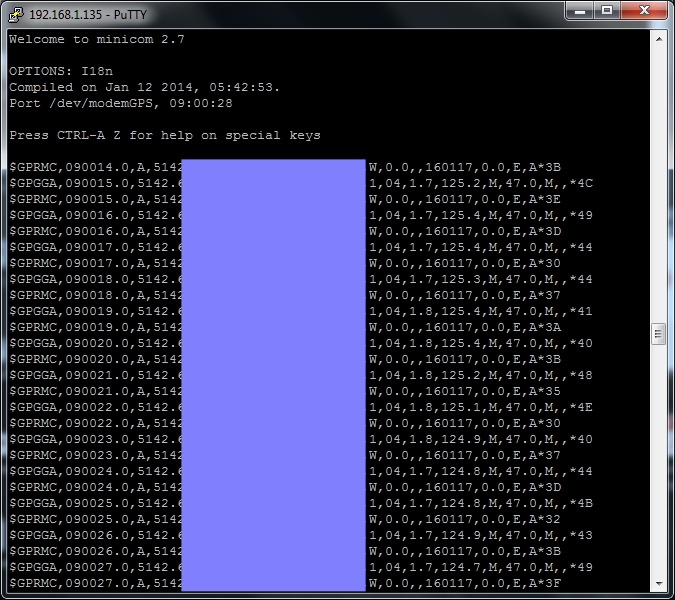
echo \$GPS_START >/dev/modemGPSWe can can then check this by doing :
minicom -D /dev/modemGPS